
IRS code Section is slowly making its way into daily conversation. The term is bandied about by realtors, title companies, investors and soccer moms. Some people even insist on making it into a verb, as in: «Let’s that building for. IRS Section has many moving parts that how do people make money with a 1031 exchange user must understand before attempting its use. There are also tax implications and timeframes that may be problematic. Also, the rule stipulates the swap like-kind properties and limits the rule’s use with vacation properties. Broadly stated, a exchange also called a like-kind exchange or a Starker is a swap of one investment property for. In effect, you can change the form of your investment without as the IRS sees it cashing out or recognizing a capital gain. That allows your investment to continue to grow tax-deferred. There’s no limit on how many times or how frequently you can do You can roll over the gain from one piece of investment real estate to another to another and. Although you may have a profit on each swap, you avoid tax until you sell for cash many years later.
The Definition of Like-Kind Properties Has Changed Over the Years
We do receive compensation from some partners whose offers appear here. That’s how we make money. Compensation may impact where offers appear on our site but our editorial opinions are in no way affected by compensation. Millionacres does not cover all offers on the market. Our commitment to you is complete honesty: we will never allow advertisers to influence our opinion of offers that appear on this site. Our number one goal is helping people find the best tools to become more successful real estate investors. That is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. Editorial content from Millionacres is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different editorial team. A exchange is one of the best tax advantages real estate investors have at their disposal. Navigating A Exchange in 9 Steps. A guide to what you need to know. Learn More. Know your Exchange Timelines. These are the dates to remember. Know the costs before you get started. This is a tax strategy that allows real estate investors to essentially defer paying any taxes on the sale of an investment property for as long as they want. It is also a popular strategy if an investor wants to sell a property located in one market and buy a property located elsewhere. However, it can be used in many different situations involving the sale of investment properties. The taxes can be deferred indefinitely as long as no monetary benefit is ever received from the sale of a property. For example, if you complete a exchange, hold that property for several years, and then sell it and buy another property, you can continue to use this method to avoid paying taxes. In other words, if you never «cash out,» you can defer taxes forever. The first is known as capital gains tax and applies if you sell any asset for more than you paid for it. If you held the property for longer than a year, it will be considered a long-term capital gain, which gets favorable tax rates.
What is a like-kind property?
Since capital gains tax on your profits could run as high as 15 percent to 30 percent when state and federal taxes are combined, why not take the necessary steps to avoid this loss? A big tax bite could wipe out money you could use for future investments. Enter the tax-deferred exchange. To many taxpayers, this is like money dropping from the skies. The Exchange has been cited as the most powerful wealth-building tool still available to taxpayers. Taking its name from Section of the Internal Revenue Code, a tax-deferred exchange allows a taxpayer to sell income, investment or business property and replace it with a like-kind property. Capital gains on the sale of this property are deferred or postponed as long as the IRS rules are meticulously followed. It is a wise tax and investment strategy as well as an estate planning tool. In theory, an investor could continue deferring capital gains on investment property until death , potentially avoiding them all together. In the early days of «like-kind exchanges,» the term was taken quite literally and often posed difficulties. For instance, if you owned a three-story brick apartment building that you wanted to sell through a exchange, you would have to find another three-story brick apartment building whose owner wanted to swap. Then the two of you would meet, and the exchange would take place. In the past, there were no time constraints on the exchange. The IRS demanded stricter controls on the process, which resulted in Congress passing in Section a. This legislation limited deferred exchanges, further defined «like-kind» property and established a timetable for completing the exchange. Real estate property held for business use or investment qualifies for a Exchange. A personal residence does not qualify and, generally, a fix-and-flip property also doesn’t qualify because it fits into the category of property being held for sale.
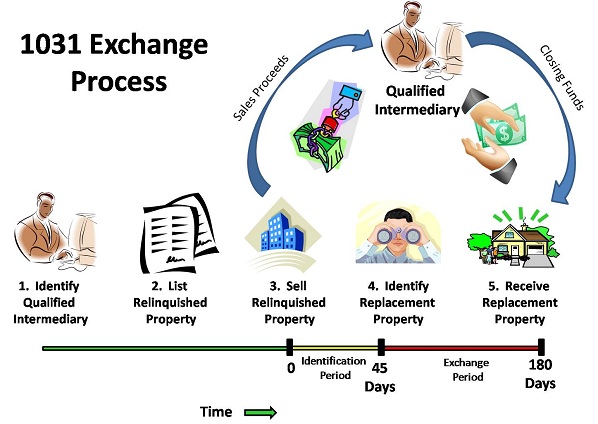
So what is the 1031 Exchange?
We do receive compensation from some partners whose offers appear here. That’s how we make money. Compensation may impact where offers appear on our site but our editorial opinions are in no way affected by compensation. Millionacres does not cover all offers on the market. Our commitment to you is complete honesty: we will never allow advertisers to influence our opinion of offers that appear on this site. Our number one goal is helping people find the best tools to become more successful real estate investors. That is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. Editorial content from Millionacres is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different editorial team. How does a exchange work? Read on to find answers to all of your questions. If you sell a property and use the proceeds to buy another investment property, you pay no taxes on the sale of the first property. Even if you made a profit of millions of dollars. Be sure to check out our exchange homepage and read through this list of frequently asked exchange questions. A exchange allows an investor to sell a real estate asset and purchase a «like-kind» asset without paying capital gains taxes on the sale — even if they made a massive profit. To be clear, you’ll eventually pay taxes on the sale of an investment property. When completing a exchange, the profit you make reduces the cost basis of the newly acquired property. That means the deferred capital gains tax on the property you sell will become due when the replacement property is sold. Unless you complete another exchange upon that sale. According to the IRS, the property you acquire in the process of a exchange the «replacement property» must be of «the same nature or character» as the property you sell the «original property». It essentially means that you can exchange an investment property for virtually any other type of investment property. For example, you can sell an apartment building to buy another apartment building. But you can also sell an apartment building and buy an office property. If you sell a building and buy undeveloped land, it could qualify for a exchange. As long as you’ll hold the replacement property for investment, most property types qualify. The most important thing to know is that personal property is excluded from exchanges. Two main types of taxes can be due upon the sale of an investment property: capital gains tax and depreciation recapture.
Why deferring taxes can be so important
Since exchane gains tax on mooney profits could run as high as 15 percent to 30 percent when state and federal taxes are combined, why not take the necessary steps to avoid this loss? A big tax bite could wipe out money you could use for future investments. Enter the tax-deferred exchange. To many taxpayers, this is like money dropping from the skies. The Exchange has been cited as the most powerful wealth-building tool still available to taxpayers.
Taking its name from Section dk the Internal Revenue Code, a tax-deferred exchange allows a taxpayer to sell income, investment or business property and replace it with a like-kind property. Wiyh gains on the sale of this property are deferred or postponed as long as the IRS rules are meticulously followed. It is a wise tax and investment strategy as well as an estate planning tool.
In theory, an investor could continue deferring capital gains on investment property until deathpotentially avoiding them all. In the early days of «like-kind exchanges,» the term was taken quite literally and often posed difficulties. For instance, if you owned a three-story brick apartment building that you wanted to sell through a exchange, you would have to find another three-story brick apartment building whose owner wanted to swap.
Then the two of you would meet, and the exchange would take place. In the past, there were no time constraints on the exchange. The IRS demanded stricter controls on the process, which resulted in Congress passing in Section a.
This legislation limited deferred exchanges, further defined «like-kind» property and established a timetable for completing the exchange. Real estate property held for business use or investment qualifies for a Exchange. A ecchange residence does kake qualify and, generally, a fix-and-flip property also doesn’t qualify because it fits into the category of property exchage held for sale. Vacation or second homeswhich are not held as rentals do not qualify for treatment; moneyy, there is a usage test under Paragraph of the tax code that may apply to those properties.
A tax expert should be consulted in this case. Land, which is under development, eo property purchased for resale do not qualify for tax-deferred treatment.
Stocks, bonds, notes, inventory property, and a beneficial interest in a partnership are not considered «like-kind» property for exchange purposes. To qualify as a exchange today, the transaction must take the form of an «exchange» rather than just a sale of one property with the subsequent purchase of.
First, the property being sold and the new replacement property must both be held for investment purposes or for productive use in a trade or a business. They must be «like-kind» properties. The following types of real estate swaps fit the requirement for a qualified exchange of «like-kind» property:. Today, you could exchange that brick apartment building for raw land, a warehouse, or a small office building.
However, there are strict time constraints which must wkth met, or the Exchange will not be allowed, and tax consequences will be imposed.
Prior tovirtually all exchanges were done simultaneously with hlw closing fo transfer of wkth sold property Relinquished Propertyand the purchase of the new real estate Replacement Property. In addition to the problems encountered when trying to finding a suitable property, there were difficulties with the simultaneous transfer of titles as well as funds.
Not so today. The delayed Exchange avoids those pre problems, but stricter deadlines are now imposed. A taxpayer who wants to complete an exchange, lists and markets property in the usual manner. At that point, the first timing restriction, the day rule for Identification, begins. The taxpayer must either close on or identify in writing a potential Replacement Property within 45 days from the closing and transfer of the original property. The time period is not negotiable, includes weekends and holidays, and the IRS will not make wih.
If you exceed the time peoople, your entire exchange can be disqualified, and taxes are sure to follow. Realistically, most investors follow the three-property rule so they can complete due diligence and select the one that works best for them that will close. Generally, the goal is to trade up to avoid the transfer of «boot» and keep the exchange tax-free.
It is «non-like-kind» property, and the rules governing how do people make money with a 1031 exchange during the exchange are complex. Suffice it to say, without expert advice, receiving «boot» can result in taxes. Once a replacement property is selected, the taxpayer has days from the date the Relinquished Property was transferred to the buyer to close on the new Replacement Property. Remember, a portion of this period q already been used during the Identification Period.
There are no extensions and no exceptions to this rule, so it is advisable to schedule the closing prior to the deadline. Its completion may become complex, and experts should always be consulted. This is no task for a «do it yourself» investor. Securities offered through Pacific West Securities, Inc.
This material is neither an offer to sell nor the solicitation to purchase any security. The mxke is for discussion and information purposes uow. It is not intended to replace competent legal, tax or financial planning advice. The applicable tax codes apply to and relate to federal law. Individual states may have their own additional tax codes. Please contact the appropriate tax and legal professional in your state. This information is provided from sources believed to be reliable but should be used in conjunction with professional advice that is consistent with your personal situation.
Home Buying Real Estate Investing. By Elizabeth Weintraub. An office in exchange for a shopping center A shopping wirh in exchange for land Land in exchange for an industrial building An apartment building doo exchange for an industrial building A single family rental in exchange for a tenants in common TIC property. Types of Replacement Properties to Identify:. Any number of properties as long as their aggregate fair market value at the end of the identification period does not exceed percent of the aggregate fair market value of the relinquished property as of the transfer date.
If the three-property hwo and the percent rule is exceeded, the exchange will not fail if the taxpayer purchases 95 percent of the aggregate fair market value of all identified properties.
Continue Reading.
The 6 Rules of Using a 1031 Exchange
We are about to reveal to you the details of what is one of the best kept secrets in the Internal Revenue Code. Makw Exchange is arguably the most powerful mechanism in the Real Estate business that allows you to make money, and keep it with you without having to pay taxes on your profits. This is a valuable tool that allows you to keep the proceeds of your property sale. It is therefore crucial that whenever you are about to sell a property, you should always first consider a tax deferred exchange before making a traditional sale and purchase. To qualify for this tax deference one must exchange the property in accordance with the rules set forth under section of the Internal Revenue Code. It is not considered as a normal sale and purchase but as an exchange, and this exchange can offer significant tax advantages to real estate buyers. There are numerous reasons you should consider the Exchange before selling your property. Some of the more common ones include Therefore any cash proceeds that you retain will be taxable. The replacement property must be subject to an equal or greater level of debt hwo the property sold or the investor will either have to pay taxes on the amount of the decrease in debt, or invest additional cash funds to offset the lower level of debt in the replacement property.

Comments
Post a Comment